Table of Contents
| Introduction |
| Intra-Site and Inter-Site Replication |
| The Schedule Attribute |
| PowerShell Script to Update the Replication Schedule |
| See Also |
| Other Resources |
Introduction
Connection objects in Active Directory (AD) specify how updates replicate between domain controllers or sites. These objects have a schedule attribute that specifies when replication is scheduled between the replication partners. This article describes a PowerShell script to modify the schedule attribute.
Intra-Site and Inter-Site Replication
Intra-site replication is replication of Active Directory updates between Domain Controllers (DCs) within an Active Directory site. These objects are in the Site container in the Configuration partition of Active Directory. For example, the distinguished name of an intra-site connection object would be similar to.
cn=<GUID>,cn=NTDS Settings,cn=MyServerA,cn=Servers,cn=MySite,cn=Sites,cn=Configuration,dc=MyDomain,dc=com
where <GUID> is a unique GUID. Intra-site connection objects created by an administrator will have a name selected by the administrator.
Inter-site replication is replication of Active Directory updates between two Active Directory sites. A typical inter-site connection object will have a distinguished name similar to.
cn=SiteA-SiteB,cn=IP,cn=Inter-Site Transports,cn=Sites,cn=Configuration,dc=MyDomain,dc=com
The Schedule Attribute
The schedule attribute is a byte array, documented in this Wiki article.
Active Directory: Document Connection Object Schedules
The article also describes a PowerShell script, GetSchedule.ps1, to document the schedule attribute of any connection object.
PowerShell Script to Update the Replication Schedule
A PowerShell script has been developed to update the replication schedule assigned to any connection object in Active Directory. The script, SetSchedule.ps1, is linked here.
Update Replication Schedule of Active Directory Connection Object
The script accepts the following parameters:
- -Site: The name (RDN) of the site where the connection object for intra-site replication is located.
- -ToServer: The NetBIOS name of the destination server in the site (intra-site replication).
- -FromServer: The NetBIOS name of the source server in the site (intra-site replication).
- -Name: The name (RDN) of a connection object for inter-site replication.
- -DN: The distinguished name of a connection object (intra-site or inter-site), in quotes.
- -CSVFile: A CSV file that specifies the replication schedule to be assigned, in local time.
In addition, the script accepts the following switch parameters:
- -Key: Outputs a table of possible schedule values each hour in decimal, hex, and binary.
- -Help: Outputs a screen of help information for the script, documenting the parameters.
The required CSV file specifies the replication schedule as decimal values for each hour of each day of the week in local time. The CSV file should have one line for each day of the week, plus a header line. The header line will be the 24 digits 0 through 23, comma separated, representing the hours in a day. Each subsequent line needs 24 comma separated decimal values. The table generated by the -Key parameter documents the meaning of the decimal values. The table is shown below. The decimal values are needed in the CSV file to specify when replication is scheduled each hour of each day.
| Decimal | Hex | Binary | # / Hr. | Schedule |
| 000 | 00 | 0000 | 0 | nnnn |
| 001 | 01 | 0001 | 1 | Ynnn |
| 002 | 02 | 0010 | 1 | nYnn |
| 003 | 03 | 0011 | 2 | YYnn |
| 004 | 04 | 0100 | 1 | nnYn |
| 005 | 05 | 0101 | 2 | YnYn |
| 006 | 06 | 0110 | 2 | nYYn |
| 007 | 07 | 0111 | 3 | YYYn |
| 008 | 08 | 1000 | 1 | nnnY |
| 009 | 09 | 1001 | 2 | YnnY |
| 010 | 0A | 1010 | 2 | nYnY |
| 011 | 0B | 1011 | 3 | YYnY |
| 012 | 0C | 1100 | 2 | nnYY |
| 013 | 0D | 1101 | 3 | YnYY |
| 014 | 0E | 1110 | 3 | nYYY |
| 015 | 0F | 1111 | 4 | YYYY |
The decimal value "2" means that replication is scheduled during the second 15 minute interval after the hour. The schedule is shown as "nYnn" in the table. The 15 minute intervals are shown chronologically, from left to right in the last column above. "Y" means replication is scheduled, "n" means replication is not scheduled.
You can use the PowerShell script GetSchedule.ps1 with the -CSV parameter to output the current schedule assigned to any connection object. You can redirect the output to a file with csv extension, and use the file as a template to specify the schedule desired. Modify the decimal values as required, then specify the file with the -CSVFile parameter of SetSchedule.ps1 to update the schedule.
An example CSV file would be similar to below.
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23
0,1,10,11,0,1,5,15,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
0,2,10,11,0,12,13,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
When this schedule is applied to an intra-site connection object, the schedule appears below in Active Directory Sites and Services.
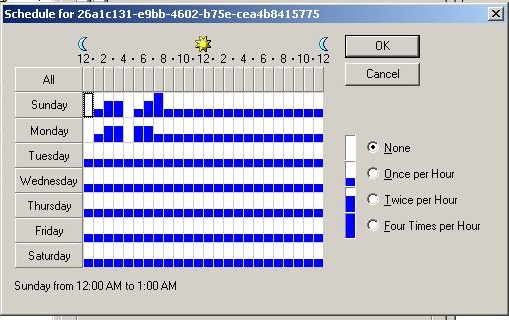
The schedule specified by the CSV file is more detailed (and accurate) than the GUI can display. For example, the sample CSV shows the value "11" specified for the fourth hour of Sunday (from 03:00 to 03:59 am). This means replication is scheduled during the first, second, and fourth 15 minute intervals after the hour. But the GUI can only show that replication is scheduled twice during the hour. The GUI has no way to display replication three times in an hour.
See Also
Active Directory: Document Connection Object Schedules
How Active Directory Replication Works
Set Active Directory To "Use notify" Replication
Other Resources
Active Directory Replication Traffic
Active Directory Replication Technologies
Active Directory Replication Tools and Settings
How Active Directory Replication Topology Works
Active Directory Replication Concepts
Advanced Active Directory Replication and Topology Management Using Windows PowerShell (Level 200)
Active Directory Replication: Change Notification & You (blog post)
Document Replication Schedule of Active Directory Connection Object (PowerShell script)
Update Replication Schedule of Active Directory Connection Object (PowerShell script)